A Stack at MMC and LMC
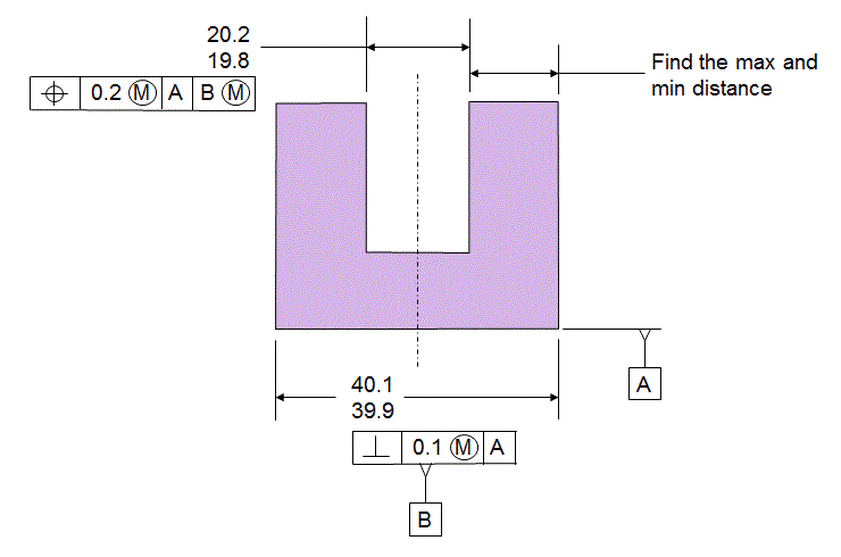
Consider the stack below. The slot is called out MMC with the datum referenced MMB. The datum itself has a perpendicularity callout at MMC.
Consider the stack below. The slot is called out MMC with the datum referenced MMB. The datum itself has a perpendicularity callout at MMC.
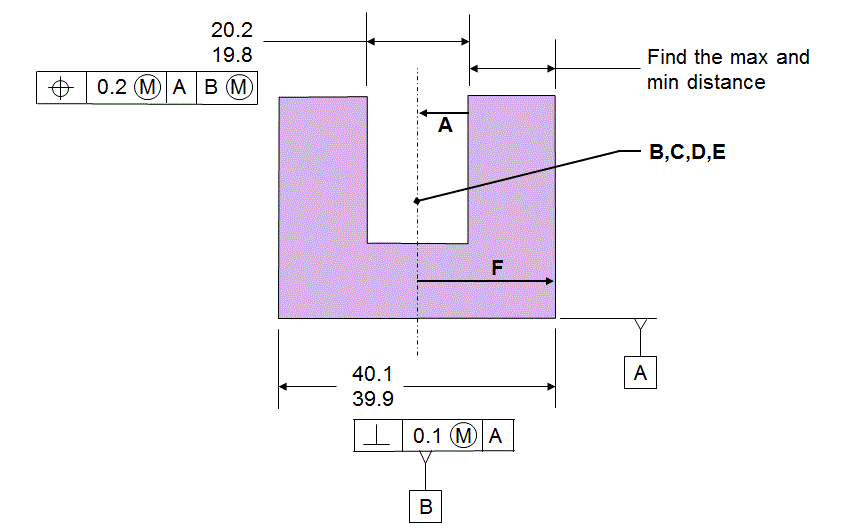
The stack path is shown below
And here is the stack
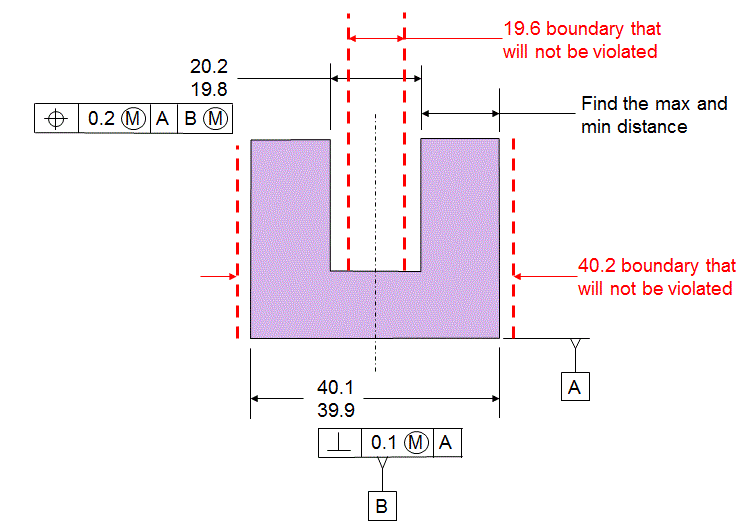
Since the Features Of Size are called out MMC and MMB, there are boundaries outside the material that will not be violated.
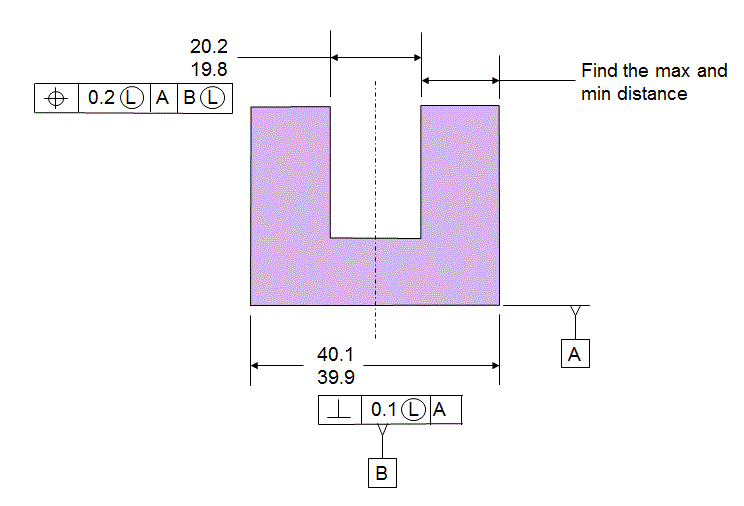
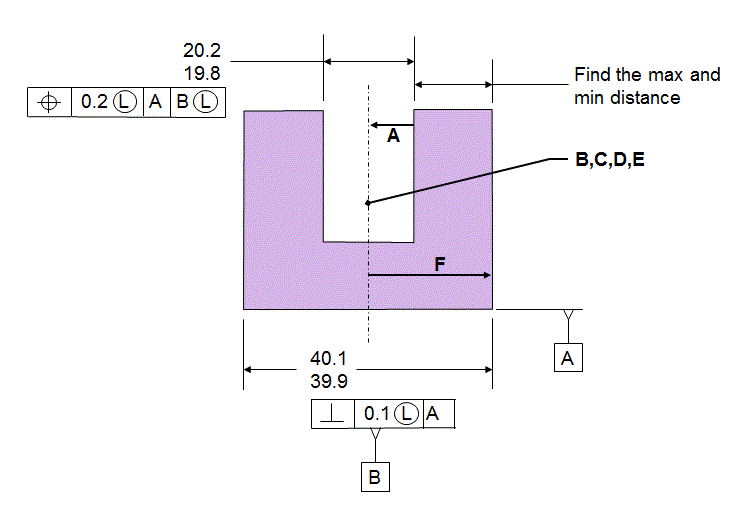
Now consider the same stack with the Features Of Size called out LMC and LMB
The stack path has not changed
The stack itself has changed
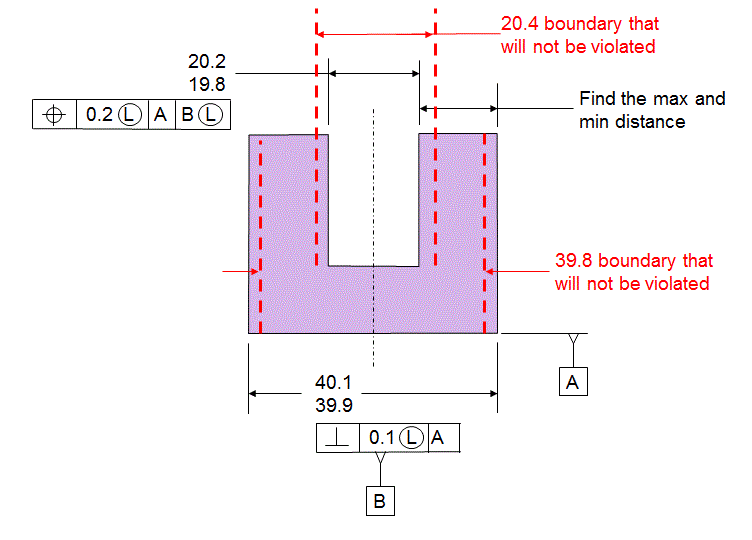
The boundaries that are being protected are now inside the material.
If you compare the results of the two stacks, you will notice that the LMC stack has a larger max value. That is because the MMC stack is protecting boundaries outside the material while the LMC stack does not respect any boundaries outside the material.
Likewise the LMC stack also has a larger min value. That is because the LMC stack is protecting a boundary inside the material while the MMC stack does not respect any boundary inside the material. This is why LMC is used for protecting a wall thickness while MMC is used for protecting boundaries that are outside the material.
Likewise the LMC stack also has a larger min value. That is because the LMC stack is protecting a boundary inside the material while the MMC stack does not respect any boundary inside the material. This is why LMC is used for protecting a wall thickness while MMC is used for protecting boundaries that are outside the material.